新闻中心
干细胞临床试验汇总
皮下注射干细胞2500万或5000万个!高剂量组效果更佳,34名患者症状明显减轻
引言
已有多项临床前研究表明,间充质干细胞可以有效发挥免疫调节作用,以治疗因Th2 型免疫过度激活而导致的特异性皮炎。本文通过分析文献,帮助大家了解间充质干细胞治疗特应性皮炎的益处以及临床结果。34 名患有中度至重度特应性皮炎的成年患者进行了皮下注射间充质干细胞后,均可观察到症状的改善,相对于低剂量组(2.5×10^ 7);高剂量组(5×10 ^7个细胞)的效果更佳。

湿疹,你了解多少?
案例分享:间充质干细胞有效改善湿疹症状
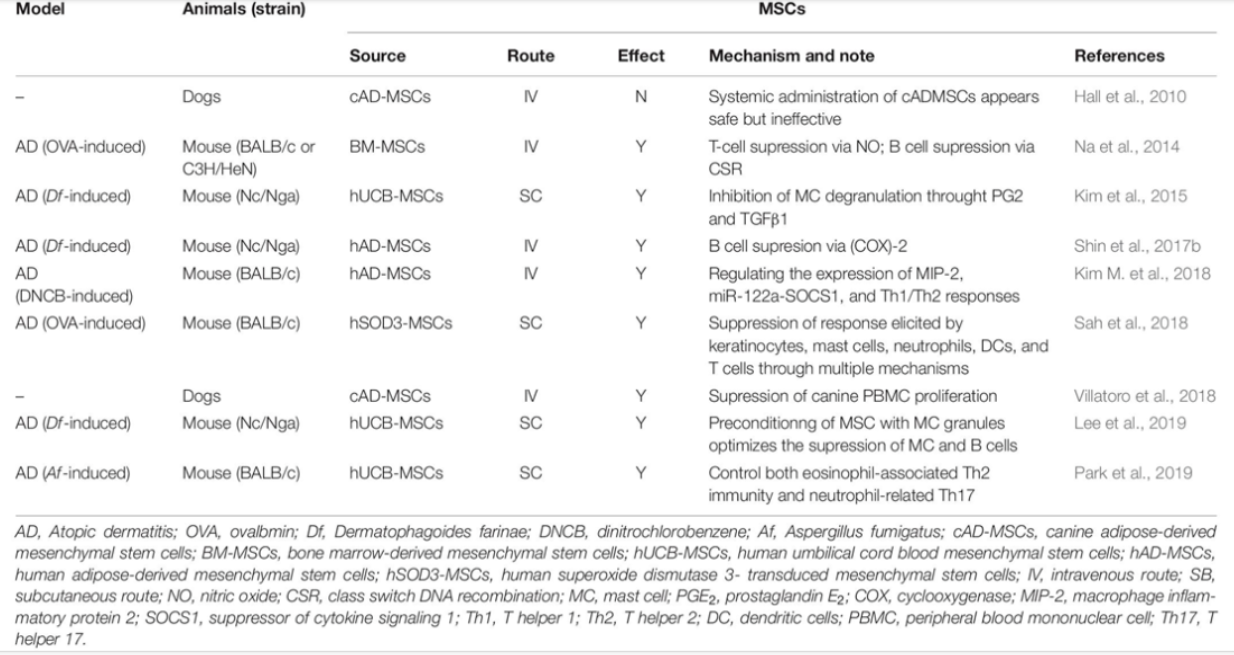
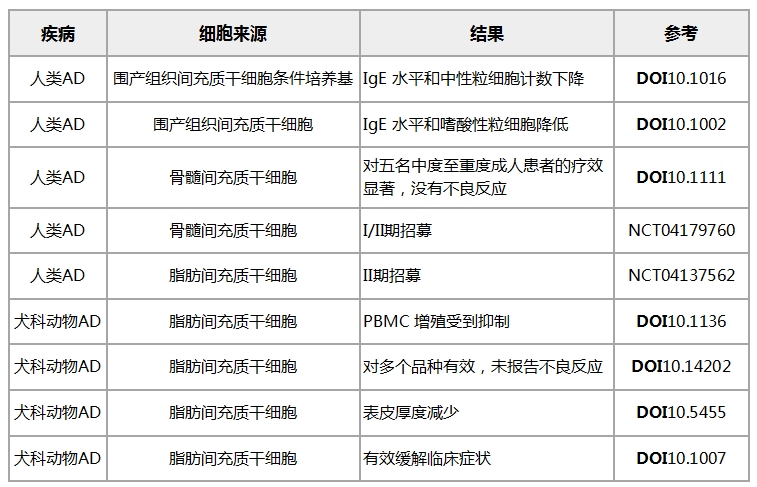
表格引用自文献11
凭借调节先天性和适应性免疫系统的能力,间充质干细胞成为治疗免疫相关性疾病的有力工具。临床前研究中产生的治疗功效和作用机制的证据表明,基于间充质干细胞的细胞疗法是治疗特应性皮炎的一种有前途的方法。无论是在动物试验,还是人体临床试验,均显示出了间充质干细胞有潜力帮助特应性皮炎患者改善病情,未来,间充质干细胞在治疗免疫相关性疾病领域的研究将继续扩大。对于患者而言,无疑这是值得期待的事。
参考文献
[1] Chaudhary, S. K., Singh, S. K., Kumari, P., Kanwal, S., Soman, S. P., Choudhury, S., et al. (2019). Alterations in circulating concentrations of IL-17, IL-31 and total IgE in dogs with atopic dermatitits. Vet. Dermatol. 30:383-e114. doi: 10.1111/vde.12762
[2] Daltro SRT, Meira CS, Santos IP, Ribeiro Dos Santos R, Soares MBP. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Atopic Dermatitis: A Review. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 14;8:326. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00326. PMID: 32478072; PMCID: PMC7240073.
[3] Ring, J., Alomar, A., Bieber, T., Deleuran, M., Fink-Wagner, A., Gelmetti, C., Gieler, U., Lipozencic, J., Luger, T., Oranje, A.P., Schäfer, T., Schwennesen, T., Seidenari, S., Simon, D., Ständer, S., Stingl, G., Szalai, S., Szepietowski, J.C., Taïeb, A., Werfel, T., Wollenberg, A. and Darsow, U. (2012), Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) Part I. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 26: 1045-1060.
[4] Meagher, L. J., Wines, N. Y., and Cooper, A. J. (2002). Atopic dermatitis: review of immunopathogenesis, and advances in immunosuppressive therapy. Australas. J. Dermatol. 43, 247–254. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0960.2002.00610.x
[5] Poggi, A., and Zocchi, M. R. (2019). Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells: still unresolved “Yin and Yang”. Curr. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 14, 344–350. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666181205115452
[6] Golchin, A., Farahany, T. Z., Khojasteh, A., Soleimanifar, F., and Ardeshirylajimi, A. (2019). The clinical trials of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in skin diseases: an update and concise review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14, 22–33. doi: 10.2174/1574888X13666180913123424
[7] Loukogeorgakis, S. P., and De Coppi, P. (2017). Concise review: amniotic fluid stem cells: the know, the unknow, and potential regenerative medicine applications. Stem Cells 35, 1663–1673. doi: 10.1002/stem.2553
[8] Lu, L. L., Liu, Y. J., Yang, S. G., Zhao, Q. J., Wang, X., Gong, X., et al. (2006). Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica 91, 1017–1026.
[9] Na, K., Yoo, H. S., Zhang, Y. X., Choi, M. S., Lee, K., Yi, T. G., et al. (2014). Bone marrow-derived clonal mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ovalbumin-induced atopic dermatitis. Cell Death Dis. 5:e1345. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.299
[10] Kim, H. S., Lee, J. H., Roh, K. H., Jun, H. J., Kang, K. S., and Kim, T. Y. (2017). Clinical trial of human umbilical cord blood-derived stem cells for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: phase I/IIa studies. Stem Cells 35, 248–255. doi: 10.1002/stem.2401
[11] Najera J, Hao J. Recent advance in mesenchymal stem cells therapy for atopic dermatitis. J Cell Biochem. 2023 Feb;124(2):181-187. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30365. Epub 2022 Dec 28. PMID: 36576973.




